Warning
You are currently viewing v2.17 of the documentation and it is not the latest. For the most recent documentation, kindly click here.
KEDA is a tool that helps Kubernetes scale applications based on real-world events. It was created by Microsoft and Red Hat. With KEDA, you can adjust the size of your containers automatically, depending on the workload—like the number of messages in a queue or incoming requests.
It’s lightweight and works alongside Kubernetes components like the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA). It doesn’t replace anything but adds more functionality. You can choose which apps to scale with KEDA while leaving others untouched. This makes it flexible and easy to integrate with your existing setup.
KEDA monitors external event sources and adjusts your app’s resources based on the demand. Its main components work together to make this possible:
In simple terms, KEDA listens to what’s happening outside Kubernetes, fetches the data it needs, and scales your apps accordingly. It’s efficient and integrates well with Kubernetes to handle scaling dynamically.
The diagram below shows how KEDA works in conjunction with the Kubernetes Horizontal Pod Autoscaler, external event sources, and Kubernetes’ etcd data store:
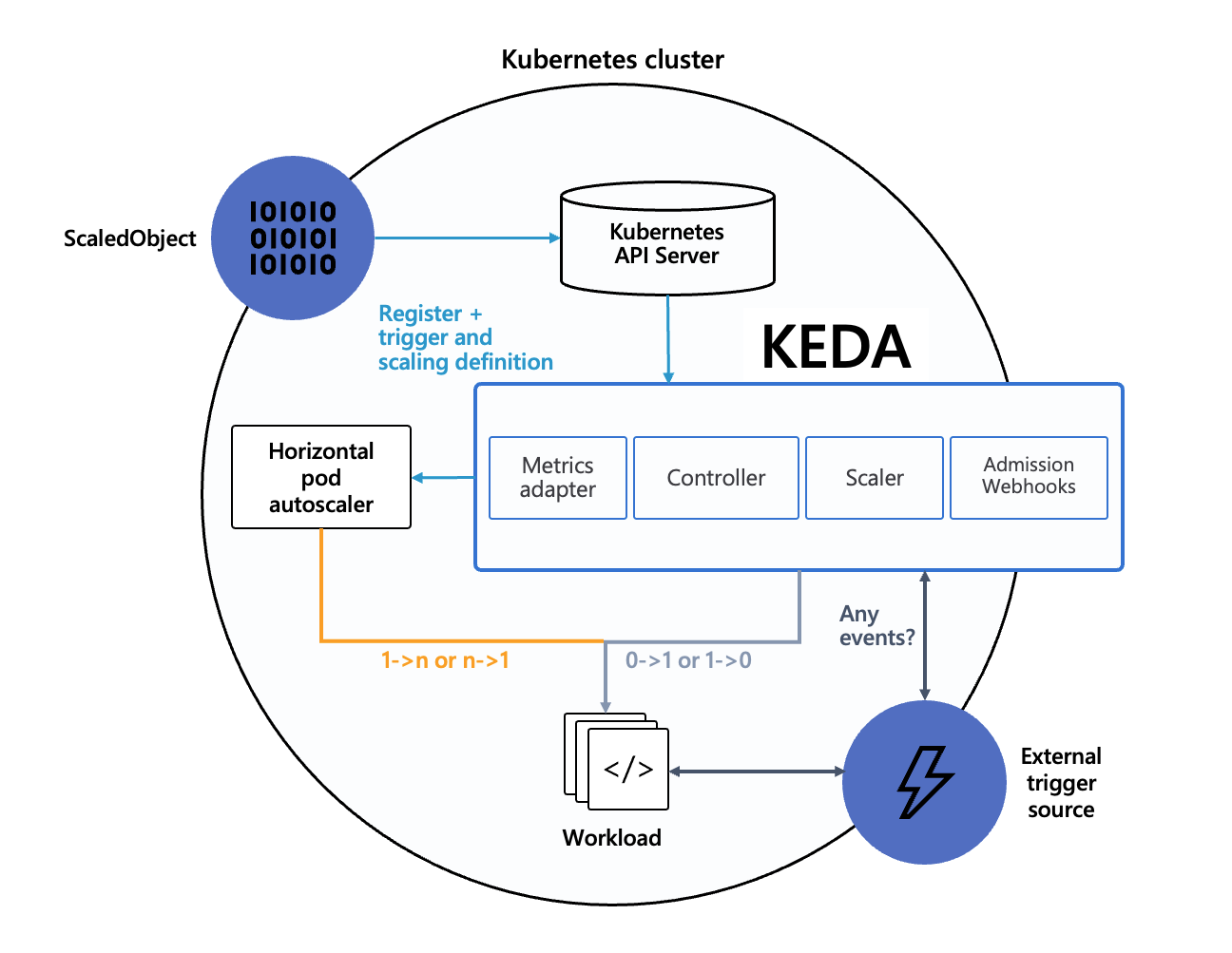
External events, like an increase in queue messages, trigger the ScaledObject, which sets the scaling rules. The Controller handles the scaling, while the Metrics Adapter sends data to the HPA for real-time scaling decisions. Admission Webhooks ensure your configuration is correct and won’t cause problems.
This setup lets Kubernetes adjust resources automatically based on what’s happening outside, keeping things efficient and responsive.
KEDA uses Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) to manage scaling behavior:
These CRDs give you control over scaling while keeping your apps secure and responsive to demand.
KEDA goes beyond CPU or memory-based scaling by connecting to external data sources like message queues, databases, or APIs. This means your apps scale in real-time based on actual workload needs.
With KEDA, you can scale Deployments and StatefulSets easily. By creating a ScaledObject, you link your workload to an event source, like a queue or request rate. KEDA adjusts the number of instances based on demand.
Deployments are perfect for stateless apps that need quick scaling. StatefulSets are great for apps requiring stable storage or identity, like databases. KEDA ensures your resources are used efficiently while keeping up with demand.
KEDA also supports custom Kubernetes resources. You set up a ScaledObject tailored to your resource and connect it to an event trigger, like database changes. From there, you define the scaling limits, and KEDA handles the rest, ensuring your custom app scales dynamically.
KEDA can scale Kubernetes Jobs for batch processing. By creating a ScaledJob, you link the task to an external event, like queue size. KEDA adjusts the number of job instances in real-time, cleaning up completed jobs automatically. This ensures you only use resources when needed.
KEDA supports secure connections to external event sources using TriggerAuthentication. You can configure it to work with secrets, cloud-native authentication like AWS IAM role, or Azure Active Directory. This keeps your connections secure and your data safe.
KEDA connects to various services, like message queues or cloud APIs, through scalers. These fetch real-time metrics to determine when and how to scale. KEDA includes built-in scalers for popular services, but you can create custom ones if needed. This lets your workloads respond to real-world demand effortlessly.
KEDA uses admission webhooks to validate your scaling setup. They ensure your configuration is correct, like preventing multiple ScaledObjects from targeting the same app. This reduces errors and makes scaling smoother.